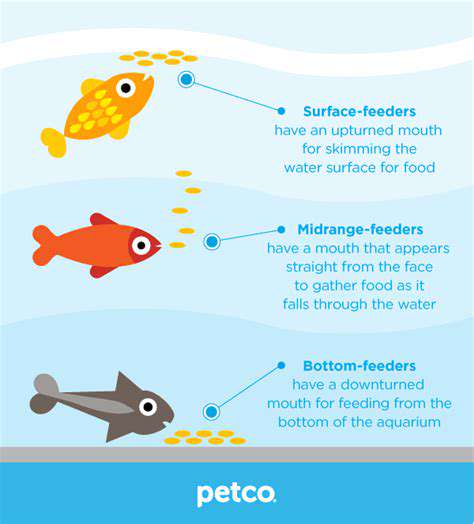
Common Cat Illnesses and Their Symptoms
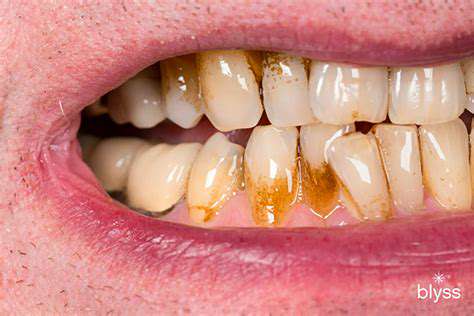
Dental Caries: Tooth Decay
Dental caries, commonly known as tooth decay, is a widespread oral health problem that affects individuals of all ages. It's a progressive disease caused by the interaction of bacteria, food, and time. These bacteria produce acids that erode the tooth enamel, eventually leading to cavities and significant pain. Early detection and intervention are crucial to preventing the spread of decay and the development of more severe complications.
Multiple factors contribute to the development of caries, including poor oral hygiene practices. Regular brushing and flossing are essential in removing plaque and food particles from the teeth, preventing the buildup of harmful bacteria. A diet high in sugary and acidic foods and drinks also plays a significant role in the process.
Gum Diseases: Periodontitis
Gum diseases, including gingivitis and periodontitis, represent a significant threat to the health of your gums and teeth. Gingivitis, the initial stage, is characterized by inflammation and bleeding of the gums. Left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more severe condition that leads to the destruction of the tissues supporting the teeth.
Periodontitis is a serious infection that can affect the bones, ligaments, and gums surrounding the teeth. The result is often tooth loss, and the progression can be insidious, often without obvious symptoms in the early stages. Early intervention and professional care are crucial to preventing further damage and preserving your oral health.
Tooth Abscesses: Localized Infection
A tooth abscess is a localized infection that develops in the pulp of a tooth or the tissues surrounding it. These infections can be extremely painful and, if left untreated, can spread to other parts of the body. Pain, swelling, and sensitivity to hot or cold are common symptoms of an abscess. Prompt treatment by a dentist is essential to alleviate the pain and prevent complications.
The severity of the abscess can vary greatly, depending on the location and extent of the infection. In some cases, a root canal procedure or even tooth extraction may be necessary to effectively eliminate the infection and prevent further damage. Ignoring a tooth abscess can have serious consequences for your overall health.
Oral Cancer: A Serious Threat
Oral cancer, while less prevalent than other forms of cancer, is a serious concern. Regular dental checkups can assist in early detection and contribute to successful treatment. It's critical to be aware of the potential symptoms and to seek prompt professional help if you have concerns. Symptoms may include sores, lumps, or changes in the mouth that do not heal or persist.
Risk factors for oral cancer include tobacco use, heavy alcohol consumption, and prolonged sun exposure. Protecting yourself through preventative measures, such as avoiding or quitting smoking and alcohol, can significantly reduce your risk. Regular oral examinations are essential in identifying any suspicious changes that could indicate the presence of pre-cancerous or cancerous lesions.
Dental Trauma: Injuries to the Mouth
Accidents and injuries can cause trauma to the mouth, resulting in broken teeth, knocked-out teeth, or damage to the soft tissues. Immediate action is vital to minimize the damage and ensure the best possible outcome. In the event of a dental injury, seek emergency dental care immediately.
Prompt treatment for dental trauma can help prevent long-term complications and restore the integrity of the oral structures. Specific treatment options will depend on the nature of the injury, with procedures ranging from dental bonding to more extensive restorative work.
Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV) and Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV): Chronic Viral Infections
Understanding FeLV and FIV
Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV) and Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV) are two of the most common chronic viral infections that affect cats. While both viruses can cause significant health issues, they have different modes of transmission and effects on the immune system. Understanding these differences is crucial for cat owners to effectively manage the health of their feline companions.
FeLV is primarily spread through saliva and can be transmitted through grooming, biting, or sharing food and water dishes. In contrast, FIV is mainly spread through deep bite wounds, making outdoor and fighting tomcats particularly vulnerable. By recognizing how these viruses are transmitted, cat owners can take proactive measures to prevent infections.
Symptoms of FeLV and FIV
Both Feline Leukemia Virus and Feline Immunodeficiency Virus can present with a variety of symptoms that may not be immediately recognizable. Common signs of FeLV include persistent fever, weight loss, lethargy, and recurrent infections due to a weakened immune system. Cats with FeLV may also develop other conditions such as anemia and lymphoma, which can significantly impact their overall health.
For FIV-infected cats, symptoms might not arise for years, as the virus can remain dormant. However, these cats may eventually exhibit symptoms similar to those of FeLV, including dental issues, chronic respiratory infections, and persistent fever. Recognizing the signs early on can lead to timely veterinary intervention and care.
Diagnosis and Testing
Diagnosing FeLV and FIV is imperative for managing a cat's health effectively. Vets usually perform a simple blood test called the ELISA test, which can detect the presence of the viruses. It's advisable to have your cat tested if they display symptoms or have been in contact with an infected cat.
Regular testing can also help in maintaining the health of cats that are at risk, such as those that go outdoors or live in multi-cat households. Catching these infections early opens the door to interventions that can improve a cat's quality of life for years. Owners should consult with their veterinarian about the best testing schedules for their pets.
Treatment Options
Currently, there is no cure for either FeLV or FIV, but treatment options are available to manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for affected cats. For FeLV-positive cats, treatment often includes supportive care, such as antibiotics for infections and medications that boost the immune system. Keeping these cats indoors is crucial to minimize exposure to other infections.
In the case of FIV, treatment focuses on managing any secondary infections and may involve a regiment of medications. Regular veterinary check-ups are essential in both scenarios to track the cat's health and any progression of symptoms. Nutritional support is also vital in helping afflicted cats maintain their strength.
Preventive Measures
Prevention is critical when it comes to managing risks associated with FeLV and FIV. Vaccination can significantly reduce the risk of FeLV, so it's recommended that cats, especially those who spend time outdoors, receive this vaccine as part of their veterinary care routine. Keeping cats indoors is also an effective preventive measure to eliminate the risk of exposure to these viruses.
For FIV, the best preventive strategy is to prevent fights between cats, as this is the primary transmission method. Ensuring that cats are neutered can help reduce aggressive behaviors, thus minimizing the risk of FIV transmission. Routine vet visits and awareness about these infections play a significant role in prevention.
Living with an Infected Cat
If your cat is diagnosed with either FeLV or FIV, it's important to provide a loving and supportive environment while keeping their health a priority. While these viral infections are serious, many cats can live for several years with a good quality of life when provided with the right care. Maintaining a stress-free environment can help manage their overall health and well-being.
FeLV-positive cats should ideally be kept separate from other cats to prevent transmission. Regular check-ups and a tailored diet can help ensure they remain as healthy and comfortable as possible. Understanding their needs and limitations is important for cat owners, and being informed can help provide the best care for these beloved companions.
Read more about Common Cat Illnesses and Their Symptoms
Hot Recommendations
- Review: [Specific Brand] Small Animal Cage
- Why Rescuing Pets Saves Lives
- Best Pet First Aid Kits [What to Include]
- How to Help Stray Animals in Your Community
- Guide to Adopting a Pet When You Have Kids
- Top Reptile Heat Lamps
- Heartwarming Rescue Stories That Will Inspire You
- Review: [Specific Brand] Bird Cage
- Best Aquarium Filters [2025 Review]
- Review: [Specific Brand] Smart Litter Box