Guide to Understanding Pet X Rays
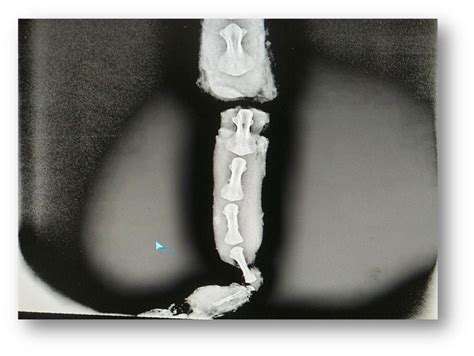
Understanding the X-Ray Image
Interpreting X-ray images requires a keen eye and a solid understanding of anatomy. X-rays provide a two-dimensional representation of a three-dimensional structure, which can be challenging to visualize and interpret. Radiologists must meticulously examine the images for subtle abnormalities and compare them to normal anatomical structures to identify potential issues. This process involves recognizing patterns, identifying densities, and assessing the overall morphology of the structures within the image.
Careful observation of the bones, tissues, and organs in the X-ray is essential. This includes evaluating the size, shape, and position of these structures against known reference points and normal variations. Any deviation from the expected appearance could indicate a problem, such as a fracture, a tumor, or a disease process.
Identifying Potential Issues
A crucial aspect of X-ray interpretation is identifying potential issues. This involves recognizing subtle changes in the density and shape of tissues and bones, which may indicate a variety of conditions. For example, an area of increased density might suggest a fracture, a tumor, or a foreign body. Conversely, an area of decreased density might signify a lung collapse, a cyst, or another pathology. Detailed knowledge of anatomical structures and potential pathologies is essential to interpreting these subtle signs.
Beyond the obvious, radiologists must also be aware of subtle indications. A slight displacement of a bone fragment or an unusual shadowing pattern can indicate a significant problem. Thoroughness and attention to detail are critical for accurate interpretation and diagnosis.
Utilizing Supporting Information
Interpreting X-rays isn't solely based on the image itself. Radiologists rely on a combination of clinical information, patient history, and other diagnostic tests to form a comprehensive understanding of the potential condition. Understanding the patient's symptoms, medical history, and the reason for the X-ray helps contextualize the findings. This process helps to differentiate between various possibilities and narrow down the potential diagnoses.
For instance, if a patient presents with severe pain in their ankle, the X-ray findings of a fracture would be more likely compared to if the patient has no symptoms. Considering all available information is vital for accurate and reliable interpretation.
Importance of Expertise and Training
The interpretation of X-ray images requires a significant amount of training and experience. Radiologists undergo extensive education and training to develop the skills needed for accurate interpretation. This includes extensive practice in identifying normal anatomy, recognizing various pathologies, and applying knowledge of different disease processes. They are constantly updated on the latest advancements in imaging technology and diagnostic techniques to ensure the accuracy of their interpretations.
The precision and accuracy of X-ray interpretation are paramount. Errors in diagnosis can have serious consequences, so it is crucial for radiologists to possess a high level of expertise and to utilize the most current knowledge and technology available to them.
Understanding the X-Ray Report
Understanding the Basics of X-Ray Imaging
X-ray imaging is a valuable diagnostic tool used to visualize the internal structures of the body, providing crucial insights into skeletal systems, organs, and other tissues. This non-invasive procedure involves exposing the area of interest to a small dose of ionizing radiation, which allows the X-ray machine to capture images of the internal structures. Understanding the basics of X-ray imaging is essential for interpreting the results and comprehending the information it provides.
Different types of X-rays can be used to target specific areas of the body, allowing for a detailed examination. This procedure is widely used in medical settings for diagnosing various conditions and injuries, offering a quick and relatively inexpensive method to assess the overall health of the patient.
Interpreting Radiographic Findings
Radiographic findings, or results from X-ray imaging, are often presented in a report, providing detailed descriptions of the images. These reports typically include descriptions of anatomical structures, their appearance, and any observed abnormalities. Understanding the terminology used in these reports is essential for effectively interpreting the findings.
The report will highlight any irregularities or abnormalities observed in the images, and it is crucial to carefully review these details to understand the implications for patient care and treatment.
Identifying Anatomical Structures
X-ray reports detail the presence and condition of various anatomical structures. These structures include bones, joints, and sometimes soft tissues, depending on the specific X-ray. Precise identification of these structures aids in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Recognizing Anomalies and Abnormalities
Anomalies and abnormalities, such as fractures, dislocations, tumors, or infections, are often highlighted in X-ray reports. These findings are critical for determining the appropriate course of action for diagnosis and treatment.
Specific descriptions of these anomalies, including location, size, and shape, are often included in the report to facilitate proper medical assessment.
Understanding the Importance of Context
The context of the patient's medical history and presenting symptoms is crucial for interpreting X-ray reports. A comprehensive understanding of the patient's condition allows for a more accurate interpretation of the findings and aids in developing an appropriate treatment plan. The radiologist will consider the clinical information alongside the X-ray images.
Reviewing the Report with a Healthcare Professional
Thorough review of the X-ray report with a healthcare professional, such as a radiologist or physician, is essential for accurate interpretation and appropriate treatment planning. This professional can explain the findings in detail, and address any questions or concerns.
Discussing the results and potential implications with the healthcare provider helps ensure that the information is understood and utilized effectively in the patient's care.
Requesting Clarification or Further Imaging
If aspects of the X-ray report are unclear or require further investigation, it's important to seek clarification from the healthcare professional. Don't hesitate to ask questions about any part of the report that you don't fully understand. Further imaging, such as CT scans or MRIs, might be necessary to gain a more complete picture of the patient's condition.
Seeking clarification from the healthcare provider is critical to ensure that the patient receives the most appropriate care and treatment based on the X-ray findings.

Read more about Guide to Understanding Pet X Rays
Hot Recommendations
- Review: [Specific Brand] Small Animal Cage
- Why Rescuing Pets Saves Lives
- Best Pet First Aid Kits [What to Include]
- How to Help Stray Animals in Your Community
- Guide to Adopting a Pet When You Have Kids
- Top Reptile Heat Lamps
- Heartwarming Rescue Stories That Will Inspire You
- Review: [Specific Brand] Bird Cage
- Best Aquarium Filters [2025 Review]
- Review: [Specific Brand] Smart Litter Box

![Review: [Specific Brand] Dog Toy [Specific Type]](/static/images/33/2025-05/ValueforMoneyandAlternatives.jpg)





![The Story of How My Dog Helped Me Through [Specific Challenge]](/static/images/33/2025-07/MoreThanJustaPet3AATrueCompanion.jpg)


