Tips for Administering Subcutaneous Fluids to Pets
Choosing the Right Equipment for Your Pet

Essential Considerations for Your Y-Axis
When selecting equipment for your Y-axis, careful consideration is crucial. Factors like the intended use, the load capacity requirements, and the precision needed significantly impact your choice. Understanding these aspects will help you avoid costly mistakes and ensure the equipment effectively meets your needs. This includes everything from the type of motor to the structural components, all of which contribute to the overall performance and longevity of the system.
Budget is also a key factor. While high-end equipment may offer superior performance and precision, it often comes with a higher price tag. You must balance your budget with the required functionality and capabilities of the Y-axis. A well-thought-out approach to your budget can help you avoid overspending and ensure you're getting the best value for your investment. This informed approach is critical for long-term success.
Precision and Accuracy in Y-Axis Design
Achieving precise and accurate movement along the Y-axis is paramount in many applications. The accuracy of the equipment directly influences the quality of the output and the overall reliability of the system. The precision of the Y-axis is critical, especially in applications requiring high-quality results. Consider the tolerances and specifications needed for your particular application, as these will dictate the appropriate equipment selections.
Using high-quality components, such as precision bearings and calibrated scales, is essential to guarantee the accuracy of the Y-axis. Thoroughly researching and evaluating different options is vital to finding the right balance between cost and performance. This research will ensure that your Y-axis meets your specific precision requirements and helps to prevent errors in your processes.
Maintenance and Durability of Your Y-Axis System
The durability and maintenance requirements of the Y-axis equipment are critical long-term considerations. Choosing equipment known for its robust construction and ease of maintenance will save you time and money in the long run. Factors like the operating environment and anticipated usage frequency play a significant role in determining the necessary level of durability. Consider the potential for wear and tear and the ease of accessing components for maintenance to minimize downtime.
Regular maintenance procedures and a proactive approach to potential issues can significantly extend the lifespan of your Y-axis system. Investing in preventative maintenance, such as lubrication schedules and component inspections, is crucial for optimal performance and avoiding costly repairs or replacements. This proactive approach will help you keep your Y-axis operating at peak efficiency for many years.
Administering the Fluids Safely and Effectively
Safe Fluid Administration Practices
Administering subcutaneous fluids safely and effectively requires meticulous attention to detail at every step. Proper preparation of the solution, careful selection of the injection site, and precise administration technique are crucial to avoid complications such as infection, tissue damage, and infiltration. Always double-check the patient's identification and the prescribed medication against the order sheet before initiating the procedure. This critical step helps prevent errors and ensures the correct medication is administered to the correct patient.
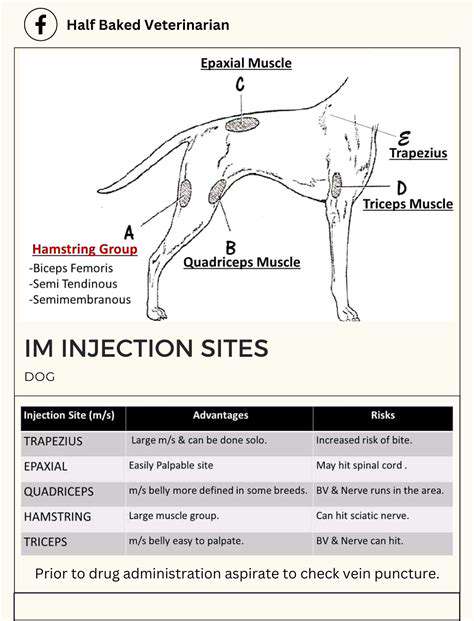
Choosing the Right Injection Site
Selecting an appropriate injection site is vital for safe subcutaneous fluid administration. Avoid areas with impaired circulation, inflammation, or recent injury. Look for subcutaneous tissue that is relatively free of bruising or scarring. Sites such as the outer aspect of the upper arms, the anterior thighs, and the abdomen are often suitable choices. Consider the patient's body habitus and the volume of the fluid to be administered when making your site selection. A larger volume may necessitate a larger, more easily accessible site.
Preparing the Solution and Equipment
Proper preparation of the solution and equipment is fundamental to ensuring the safety and efficacy of the subcutaneous fluid administration. Always verify the solution's expiration date and check for any signs of discoloration or particulate matter. Ensure the necessary equipment, such as syringes, needles, and alcohol swabs, is sterile and in good working order. Using aseptic technique throughout the process is essential to prevent contamination and infection. The use of sterile gloves further minimizes the risk of cross-contamination.
Monitoring for Complications
Continuous monitoring for complications is crucial during and after subcutaneous fluid administration. Closely observe the injection site for any signs of swelling, redness, pain, or leakage. Infiltration, where the fluid leaks into surrounding tissues, is a potential complication and should be addressed promptly. If any adverse reactions occur, stop the administration immediately and notify the appropriate healthcare professional. Document all observations, including the time, nature of any reactions, and any interventions undertaken.
Patient Education and Communication
Effective patient education and clear communication are vital components of safe subcutaneous fluid administration. Educate the patient about the procedure, including the purpose of the fluid, potential side effects, and the importance of reporting any discomfort. Clearly explain the signs and symptoms to watch for and emphasize the importance of promptly reporting any unusual sensations or changes in the injection site. Establish a clear communication channel with the patient throughout the entire process to ensure their comfort and safety.
Important Considerations and Precautions
Proper Patient Assessment
Before initiating subcutaneous fluid therapy, a thorough patient assessment is crucial. This includes evaluating the patient's overall health status, medical history, and any potential contraindications to subcutaneous fluid administration. Assessing the patient's hydration status, including skin turgor, mucous membrane moisture, and vital signs, is essential to determine the appropriate fluid type and volume. A detailed understanding of the patient's current medication regimen is also vital to avoid potential drug interactions or adverse effects.
Careful consideration of the patient's underlying conditions, such as kidney disease or heart failure, is paramount. These conditions can significantly impact fluid tolerance and necessitate adjustments to the administration protocol. Documenting all pertinent information, including the patient's weight, height, and any allergies, is critical for accurate record-keeping and potential future reference.
Choosing the Appropriate Fluid
Selecting the correct subcutaneous fluid is critical for safe and effective therapy. Different fluids are formulated for different purposes, and the choice depends on the patient's specific needs. Isotonic fluids, such as saline solutions, are often preferred for their balanced electrolyte composition and minimal risk of adverse effects. However, the specific needs of the patient should always be considered, including any existing electrolyte imbalances or ongoing medical conditions.
Site Selection and Preparation
Proper site selection and preparation are essential to prevent complications like infection or tissue damage. The injection site should be free from any lesions, inflammation, or edema. The skin should be cleansed thoroughly with an antiseptic solution before injection to minimize the risk of infection. The preferred sites for subcutaneous fluid administration often include the upper arms or thighs, ensuring adequate subcutaneous tissue for optimal fluid absorption. Careful consideration of the patient's body habitus and any existing skin conditions is vital.
Fluid Administration Technique
Administering subcutaneous fluids requires meticulous technique to ensure proper absorption and avoid complications. The fluid should be injected slowly and steadily, avoiding rapid or forceful injections that could lead to discomfort or tissue damage. Using a suitable gauge needle and appropriate equipment is critical for proper administration. The needle should be inserted at a 45-degree angle, ensuring the needle is not too deep or too shallow.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Post-administration monitoring is vital to evaluate the efficacy of the therapy and detect any potential complications. Regular monitoring of vital signs, including blood pressure, pulse rate, and temperature, is necessary. Close observation of the injection site for any signs of inflammation, redness, or swelling is essential. Documenting all observations and responses to the therapy in the patient's medical record is crucial for tracking progress and identifying any potential issues.
Potential Complications and Management
Potential complications of subcutaneous fluid administration include infection, tissue damage, and fluid extravasation. Prompt recognition and management of these complications are crucial to ensure patient safety. Infection at the injection site can be minimized by meticulous preparation and adherence to sterile techniques. In the event of fluid extravasation, prompt intervention to limit tissue damage is critical. Understanding these possible complications and their management strategies is essential for ensuring patient safety and positive treatment outcomes. Knowing how to recognize signs of adverse reactions and how to respond appropriately is vital for safe practice.
Read more about Tips for Administering Subcutaneous Fluids to Pets
Hot Recommendations
- Review: [Specific Brand] Small Animal Cage
- Why Rescuing Pets Saves Lives
- Best Pet First Aid Kits [What to Include]
- How to Help Stray Animals in Your Community
- Guide to Adopting a Pet When You Have Kids
- Top Reptile Heat Lamps
- Heartwarming Rescue Stories That Will Inspire You
- Review: [Specific Brand] Bird Cage
- Best Aquarium Filters [2025 Review]
- Review: [Specific Brand] Smart Litter Box